Auto Deployment Using Travis CI
SUSI Web Chat uses Travis CI with a custom build script to deploy itself on gh-pages after every pull request is merged into the project. The build system auto updates the latest changes hosted on chat.susi.ai. In this blog, we will see how to automatically deploy the repository on gh pages.
To proceed with auto deploy on gh-pages branch,
- We first need to setup Travis for the project.
- Register on https://travis-ci.org/ and turn on the Travis for this repository.
Next, we add .travis.yml in the root directory of the project.
#!/bin/bash
SOURCE_BRANCH="master"
TARGET_BRANCH="gh-pages"
# Pull requests and commits to other branches shouldn't try to deploy.
if [ "$TRAVIS_PULL_REQUEST" != "false" -o "$TRAVIS_BRANCH" != "$SOURCE_BRANCH" ]; then
echo "Skipping deploy; The request or commit is not on master"
exit 0
fi
# Save some useful information
REPO=`git config remote.origin.url`
SSH_REPO=${REPO/https:\/\/github.com\//git@github.com:}
SHA=`git rev-parse --verify HEAD`
ENCRYPTED_KEY_VAR="encrypted_${ENCRYPTION_LABEL}_key"
ENCRYPTED_IV_VAR="encrypted_${ENCRYPTION_LABEL}_iv"
ENCRYPTED_KEY=${!ENCRYPTED_KEY_VAR}
ENCRYPTED_IV=${!ENCRYPTED_IV_VAR}
openssl aes-256-cbc -K $ENCRYPTED_KEY -iv $ENCRYPTED_IV -in deploy_key.enc -out ../deploy_key -d
chmod 600 ../deploy_key
eval `ssh-agent -s`
ssh-add ../deploy_key
# Cloning the repository to repo/ directory,
# Creating gh-pages branch if it doesn't exists else moving to that branch
git clone $REPO repo
cd repo
git checkout $TARGET_BRANCH || git checkout --orphan $TARGET_BRANCH
cd ..
# Setting up the username and email.
git config user.name "Travis CI"
git config user.email "$COMMIT_AUTHOR_EMAIL"
# Cleaning up the old repo's gh-pages branch except CNAME file and 404.html
find repo/* ! -name "CNAME" ! -name "404.html" -maxdepth 1 -exec rm -rf {} \; 2> /dev/null
cd repo
git add --all
git commit -m "Travis CI Clean Deploy : ${SHA}"
git checkout $SOURCE_BRANCH
# Actual building and setup of current push or PR.
npm install
npm run build
mv build ../build/
git checkout $TARGET_BRANCH
rm -rf node_modules/
mv ../build/* .
cp index.html 404.html
# Staging the new build for commit; and then committing the latest build
git add -A
git commit --amend --no-edit --allow-empty
# Deploying only if the build has changed
if [ -z `git diff --name-only HEAD HEAD~1` ]; then
echo "No Changes in the Build; exiting"
exit 0
else
# There are changes in the Build; push the changes to gh-pages
echo "There are changes in the Build; pushing the changes to gh-pages"
# Actual push to gh-pages branch via Travis
git push --force $SSH_REPO $TARGET_BRANCH
fi
To find the code go to https://github.com/fossasia/chat.susi.ai/blob/master/.travis.yml
The Travis configuration files will ensure that the project is building for every change made, using npm test command, in our case, it will only consider changes made on the master branch.
If one wants to watch other branches one can add the respective branch name in travis configurations. After checking for build passing we need to automatically push the changes made for which we will use a bash script.
#!/bin/bash
SOURCE_BRANCH="master"
TARGET_BRANCH="gh-pages"
# Pull requests and commits to other branches shouldn't try to deploy.
if [ "$TRAVIS_PULL_REQUEST" != "false" -o "$TRAVIS_BRANCH" != "$SOURCE_BRANCH" ]; then
echo "Skipping deploy; The request or commit is not on master"
exit 0
fi
# Save some useful information
REPO=`git config remote.origin.url`
SSH_REPO=${REPO/https:\/\/github.com\//git@github.com:}
SHA=`git rev-parse --verify HEAD`
ENCRYPTED_KEY_VAR="encrypted_${ENCRYPTION_LABEL}_key"
ENCRYPTED_IV_VAR="encrypted_${ENCRYPTION_LABEL}_iv"
ENCRYPTED_KEY=${!ENCRYPTED_KEY_VAR}
ENCRYPTED_IV=${!ENCRYPTED_IV_VAR}
openssl aes-256-cbc -K $ENCRYPTED_KEY -iv $ENCRYPTED_IV -in deploy_key.enc -out ../deploy_key -d
chmod 600 ../deploy_key
eval `ssh-agent -s`
ssh-add ../deploy_key
# Cloning the repository to repo/ directory,
# Creating gh-pages branch if it doesn't exists else moving to that branch
git clone $REPO repo
cd repo
git checkout $TARGET_BRANCH || git checkout --orphan $TARGET_BRANCH
cd ..
# Setting up the username and email.
git config user.name "Travis CI"
git config user.email "$COMMIT_AUTHOR_EMAIL"
# Cleaning up the old repo's gh-pages branch except CNAME file and 404.html
find repo/* ! -name "CNAME" ! -name "404.html" -maxdepth 1 -exec rm -rf {} \; 2> /dev/null
cd repo
git add --all
git commit -m "Travis CI Clean Deploy : ${SHA}"
git checkout $SOURCE_BRANCH
# Actual building and setup of current push or PR.
npm install
npm run build
mv build ../build/
git checkout $TARGET_BRANCH
rm -rf node_modules/
mv ../build/* .
cp index.html 404.html
# Staging the new build for commit; and then committing the latest build
git add -A
git commit --amend --no-edit --allow-empty
# Deploying only if the build has changed
if [ -z `git diff --name-only HEAD HEAD~1` ]; then
echo "No Changes in the Build; exiting"
exit 0
else
# There are changes in the Build; push the changes to gh-pages
echo "There are changes in the Build; pushing the changes to gh-pages"
# Actual push to gh-pages branch via Travis
git push --force $SSH_REPO $TARGET_BRANCH
fi
This bash script will enable Travis CI user to push changes to gh pages, for this we need to store the credentials of the repository in encrypted form.
1. To get the public/private rsa keys we use the following command
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"
2. It will generate keys in .ssh/id_rsa folder in your home repository.
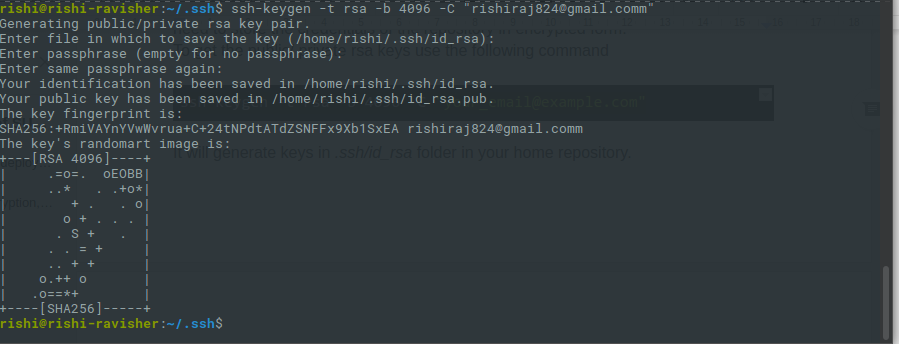
- Make sure you do not enter any passphrase while generating credentials otherwise Travis will get stuck at the time of decryption of the keys.
- Copy the public key and deploy the key to repository by visiting
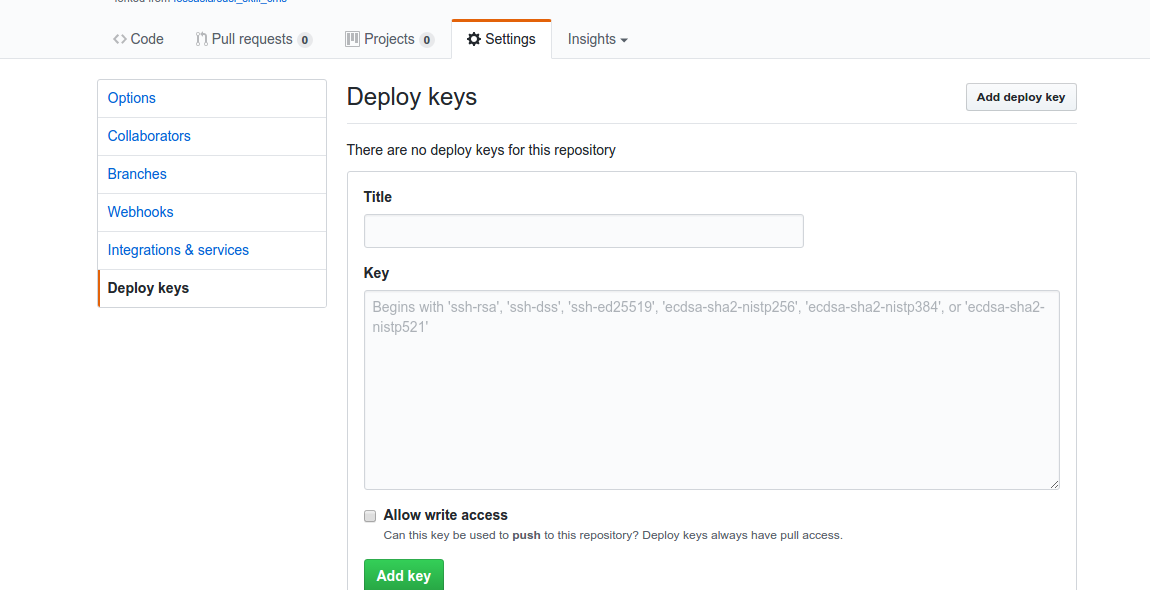
5. We also need to set the environment variable ENCRYPTED_KEY in Travis. Here’s a screenshot where to set it in the Travis repository dashboard.
6. Next, install Travis for encryption of keys.
sudo apt install ruby ruby-dev
sudo gem install travis
7. Make sure you are logged in to Travis, to login use the following command.
travis login
8. Make sure you have copied the ssh to deploy_key and then encrypt your private deploy_key and add it to root of your repository, use command -
travis encrypt-file deploy_key
9. After successful encryption, you will see a message
Please add the following to your build script (before_install stage in your .travis.yml, for instance):
openssl aes-256-cbc -K $encrypted_3dac6bf6c973_key -iv $encrypted_3dac6bf6c973_iv -in deploy_key.enc -out ../deploy_key -d
-
Add the above-generated deploy_key in Travis and push the changes on your master branch. Do not push the deploy_key only the encryption file i.e., deploy_key.enc
-
Finally, push the changes and create a Pull request and merge it to test the deployment. Visit Travis logs for more details and debugging.
Resources
- Auto deploying using Travis https://gist.github.com/domenic/ec8b0fc8ab45f39403dd#get-encrypted-credentials
- Blog on deploying a React app by Jake Weisler https://medium.freecodecamp.org/surge-vs-github-pages-deploying-a-create-react-app-project-c0ecbf317089
- How to add an ssh agent https://help.github.com/articles/generating-a-new-ssh-key-and-adding-it-to-the-ssh-agent/
- Travis CI - travis-ci.org

